| Home | Trees | Indices | Help |
|
|---|
|
|

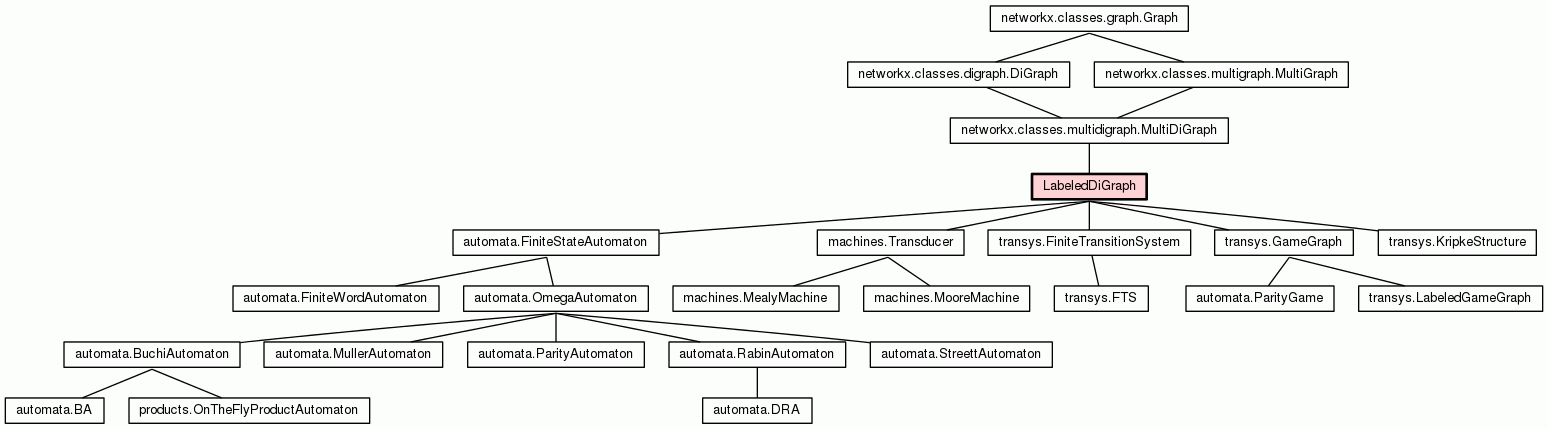
Directed multi-graph with constrained labeling.
Provides facilities to define labeling functions on vertices and edges, with given co-domains, so that labels are type-checked, not arbitrary.
Each state (or edge) is annotated with labels. Before removing a value from a label type, first make sure no state (or edge) is labeled with it.
Multiple edges with the same attr_dict are not possible.
So the difference from networkx.MultiDiGraph is that the
dict of edges between u,v is a bijection.
Between two nodes either:
but mixing labeled with unlabeled edges for the same edge is not allowed, to simplify and avoid confusion.
BEWARE: the dot interface will be separated from the class itself. Some basic style definitions as below may remain, but masking selected labels and other features will be accessible only via functions.
For dot export subclasses must define:
Note: this interface will be improved in the future.
Some code in overridden methods of networkx.MultiDiGraph is adapted from networkx, which is distributed under the BSD license.
| Instance Methods | |||
|
|||
| bool |
|
||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
| bool |
|
||
|
|||
|
Inherited from Inherited from Inherited from Inherited from Inherited from |
|||
| Properties | |
|
Inherited from Inherited from |
| Method Details |
Initialize the types of labelings on states and edges. Label types by exampleUse a >>> types = [ {'name': 'drink', 'values': {'tea', 'coffee'}, 'setter': True, 'default': 'tea'}, ] This will create a label type named Assuming this label type applies to nodes, you can now label a new node as: >>> g = LabeledDiGraph(types) >>> g.add_node(1, drink='coffee') If you omit the label when adding a new node, it gets the default value: >>> g.add_node(2) >>> g.node[2] {'drink': 'tea'} The main difference with vanilla >>> type(g.node[2]) tulip.transys.mathset.TypedDict The This allows us to add more values after creating the graph: >>> g.drink {'coffee', 'tea'} >>> g.drink.add('water') {'coffee', 'tea', 'water'} Finally, the graph will prevent us from accidentally using an
untyped label name, by raising an >>> g.add_node(3, day='Jan') AttributeError: ... To add untyped labels, do so explicitly: >>> g.add_node(3, day='Jan', check=False) >>> g.node[3] {'day': 'Jan', 'drink': 'tea'} Details on label typesEach label type is defined by a
and optionally the keys:
|
Check if labels are consistent with their type definitions. Use case: removing values from a label type can invalidate existing labels that use them.
|
Use a TypedDict as attribute dict. Log warning if node already exists. All other functionality remains the same.
|
Create or label multiple nodes. For details see add_node and
|
Use a TypedDict as attribute dict.
Each label defines a different labeled edge. So to "change" the label, either:
For more details see Notes
|
Add multiple labeled edges. For details see
|
Remove single labeled edge.
|
Remove labeled edges. Example>>> g = LabeledDiGraph() >>> g.add_edge(1, 2, day='Mon') >>> g.add_edge(1, 2, day='Tue') >>> edges = [(1, 2, {'day':'Mon'}), (1, 2, {'day':'Tue'})] >>> g.remove_edges_from(edges)
|
Return False if all nodes have outgoing edges. Edge labels are not taken into account. |
Return dot string. Requires pydot. |
Save image to file. Recommended file formats:
Any other format supported by Experimental:
Requires
and for tikz:
See Alsoplot,
|
Plot image using dot. No file I/O involved. Requires GraphViz dot and either Matplotlib or IPython. NetworkX does not yet support plotting multiple edges between 2 nodes. This method fixes that issue, so users don't need to look at files in a separate viewer during development. See AlsoDependsdot and either of IPython or Matplotlib |
| Home | Trees | Indices | Help |
|
|---|
| Generated by Epydoc 3.0.1 on Tue May 12 18:21:43 2015 | http://epydoc.sourceforge.net |